Saturday, April 25, 2015
Saturday, April 18, 2015
Replacing Consonants
Code for Replacing Consonant With the Next Consonant in the Provided String.
import java.util.Scanner; //Scanner Class
public class StringMapOne{
static String alterString(String s) //Method to Alter the String
{
int n = s.length();
char[] ar = new char[n];
ar = s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
switch(ar[i])
{
case 'b':
case 'c':
case 'd':
case 'f':
case 'g':
case 'h':
case 'j':
case 'k':
case 'l':
case 'm':
case 'n':
case 'p':
case 'q':
case 'r':
case 's':
case 't':
case 'v':
case 'w':
case 'x':
case 'y':
case 'z': int c = (int)ar[i]; //Printing the Next Letter to Consonants
c = c+1;
char d = (char)c;
ar[i] = d;
break;
default : ar[i] = ar[i];
break;
}
}
String obj = new String(ar);
return obj.toUpperCase(); //Printing in Upper Case
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Program to Perform Opeation on String");
System.out.print("Enter the String:- \t");
String z = sc.next().toLowerCase();
String b = alterString(z); //Calling the Function
System.out.println("The Output is:- \t"+b);
}
}
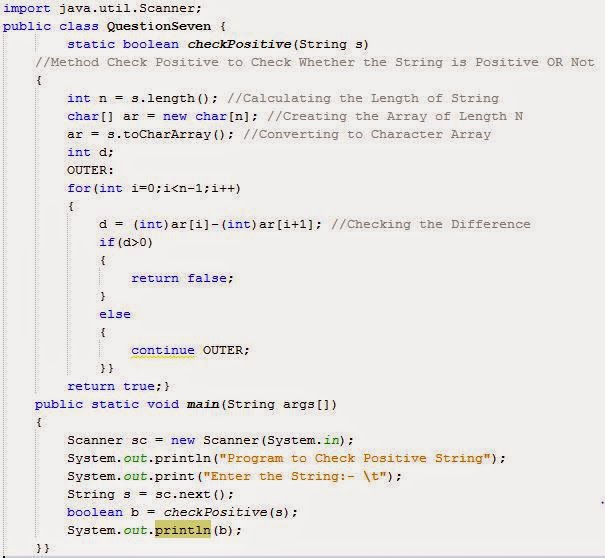
Positive Strings
Code to Check Whether the Entered String is Positive or Not.
A string is considered a positive string, if on moving from left to right each character in the String comes after the previous characters in the Alphabetical order. For Example ANT is a positive String (Since T comes after N and N comes after A) APPLE is not positive since L comes before P in the alphabetical order.Dupledrome Checking
Code to Check Whether the entered String is Dupledrome or Not.
Dupledrome means that every element present in the String should be present twice i.e., "rattar" is a dupledrome string whereas "rasrat" is not a Dupledrome String.
import java.util.Scanner; //Scanner Class
public class DupledromeChecking {
static boolean isDupledrome(String ap)
{
int N = ap.length();
char[] ar = new char[N]; //Char Array
ar = ap.toCharArray();
int i,k=0,q=0,r=0,j;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<N;j++)
{
if(ar[i]==ar[j]) //When Values are Equal
{
r++; //Increment The Count
}
}
}
/*If The Counted Value is Equal to Twice the Lenght
then it is Said that every element present
exactly twice */
if(r==(N*2))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //Scanner Object
System.out.println("Program to Check Whether the Entered String is Dupledrome or Not");
System.out.print("Enter the String:- \t");
String s1 = sc.next();
boolean result = isDupledrome(s1); //Calling Function
System.out.println("Dupledrome String:- \t"+result);
}
}
Display Strings in Between * Lines
Here is the code to display the string in the * column using loop for any string provided by user.
public class StringDisplay {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the String:- \t");
String s = sc.next(); //Getting String Input from user
int n = s.length(); //Finding Length of String
for(int i=1;i<n+5;i++) //Running Loop
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("**"+s+"**");
for(int i=1;i<n+5;i++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Funny Strings
Here is my Code to Check Whether the String is Funny Or Not.
Suppose you have a string
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FunnyString
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int T,i;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
T = sc.nextInt(); //Number of Test Cases
String[] S = new String[T];
StringBuffer[] R = new StringBuffer[T];
if(T>=1 && T<=10)
{
for(i=1;i<=T;i++)
{
S[i-1] = sc.next();
StringBuffer S1 = new StringBuffer(S[i-1]);
R[i-1] = S1.reverse();
}
}
char[] ch = null;
char[] ch1 = null;
FAST:
for(int z=1;z<=T;z++)
{
if(S[z-1].length()>=1 && S[z-1].length()<=10000)
{
OUTER:
for(i=1;i<S[z-1].length();i++)
{
ch = new char[S[z-1].length()];
ch1 = new char[S[z-1].length()];
ch = S[z-1].toCharArray();
String r = new String(R[z-1]);
ch1 = r.toCharArray();
int v = (int)(ch[i]-ch[i-1]);
int f = Math.abs(v);
int b = (int)(ch1[i]-ch1[i-1]);
int g = Math.abs(b);
if(f==g)
{
continue OUTER;
}
else
{
System.out.println("Not Funny");
continue FAST;
}
}
System.out.println("Funny");
continue FAST;
}
}
}
}
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)